Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) have revolutionized the way we navigate and position ourselves across the globe. As technology advances, Next-Gen GNSS: The Future of Global Navigation and Positioning is shaping up to be even more transformative, promising enhanced accuracy, reliability, and accessibility.
Understanding GNSS and Its Importance
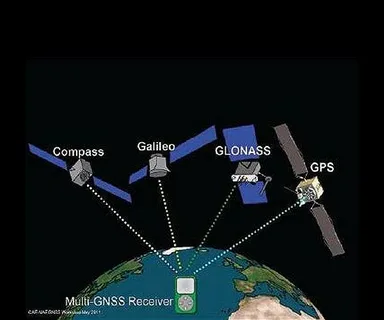
GNSS navigation refers to a constellation of satellites that provide geo-spatial positioning with global coverage. Traditional systems like the United States’ GPS, Russia’s GLONASS, Europe’s Galileo, and China’s BeiDou have become indispensable in various sectors such as transportation, agriculture, defense, and telecommunications.
However, as demands for precision and robustness grow, current systems face challenges related to signal interference, urban canyon effects, and atmospheric disturbances. This is where Next-Gen GNSS: The Future of Global Navigation and Positioning steps in, aiming to overcome these limitations.
What Defines Next-Gen GNSS?
Next-generation GNSS technologies focus on multiple innovations:
- Improved Accuracy: By integrating more satellites, advanced atomic clocks, and multi-frequency signals, next-gen systems aim to deliver centimeter-level accuracy.
- Enhanced Reliability: Techniques like satellite cross-linking and better error correction reduce signal loss and improve availability.
- Increased Security: With rising cyber threats, encryption and anti-spoofing measures are being strengthened to protect navigation data.
- Interoperability: Future GNSS platforms are designed to work seamlessly across different regional systems, ensuring global coverage and consistent performance.
Applications Driving the Future of GNSS
The impact of Next-Gen GNSS: The Future of Global Navigation and Positioning extends across various sectors:
Autonomous Vehicles and Drones
Precision positioning is critical for self-driving cars and delivery drones. Next-gen GNSS allows these systems to navigate complex environments with greater confidence and safety.
Smart Cities and IoT
As urban areas adopt smart technologies, the need for accurate location data for infrastructure, public services, and real-time analytics grows. Enhanced GNSS capabilities will support these evolving needs.
Agriculture and Environmental Monitoring
Precision agriculture relies heavily on accurate positioning for efficient resource use, while environmental monitoring benefits from reliable data for tracking changes and disaster response.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
Despite the promising advancements, challenges remain. Upgrading infrastructure, managing the increased satellite traffic, and ensuring equitable global access require international cooperation and significant investment.
Nevertheless, the momentum behind Next-Gen GNSS: The Future of Global Navigation and Positioning indicates a bright horizon where navigation is more precise, secure, and universally accessible.